AI-powered products & projects
Data Science and AI can drive true innovation, differentiate your product and help you gain a competitive edge. We are here to support you with your new project or idea, derive the specs of your AI-enabled product, make sense of emerging trends in AI and engage our data scientists and engineers to your use case.

Why choose us?
We have a long and proven track record in Machine learning research & development. We are capable of using the best of breed advances in AI and we are regularly contributing in the technological and academic developments of the field. Moreover, after we deliver, we will always be by your side to help you get the most from your technology investment and have your AI system fine-tuned and optimised.
Our data scientists will provide to you a bird’s-eye view of all technological and implementation options that fulfil your needs. Then, you will choose the best for your business, avoiding unnecessary investments and overheads.
The demonstrations below are for illustrative purposes only. They show AI-enabled applications we have been involved with.
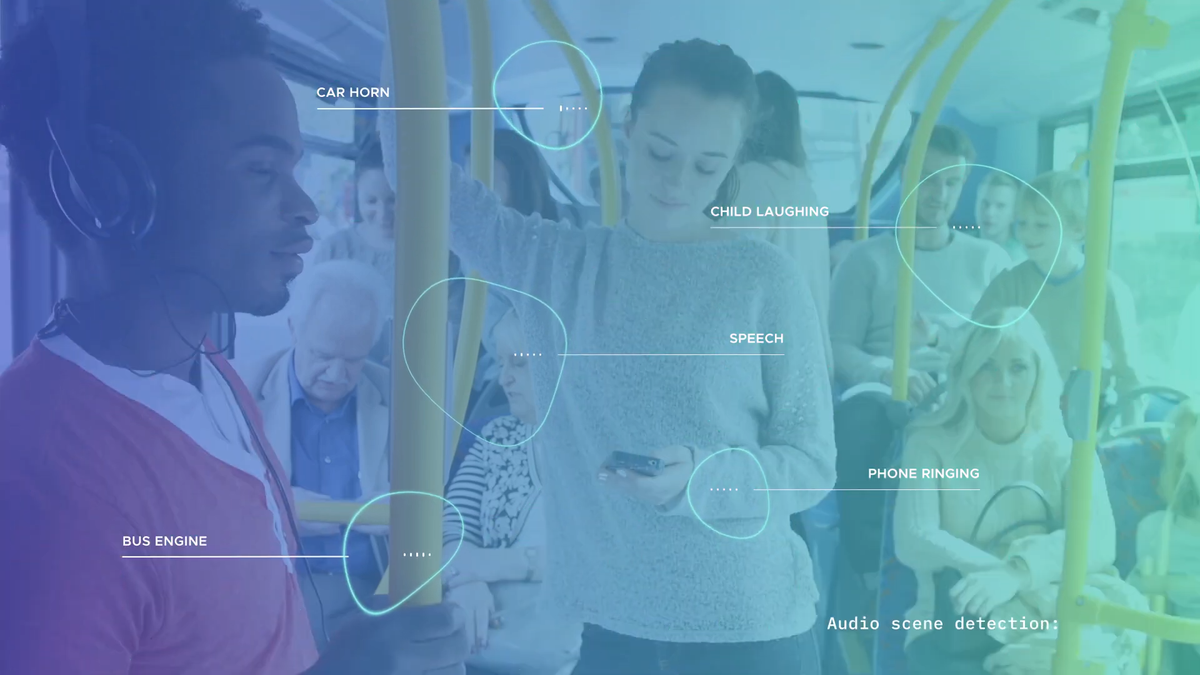
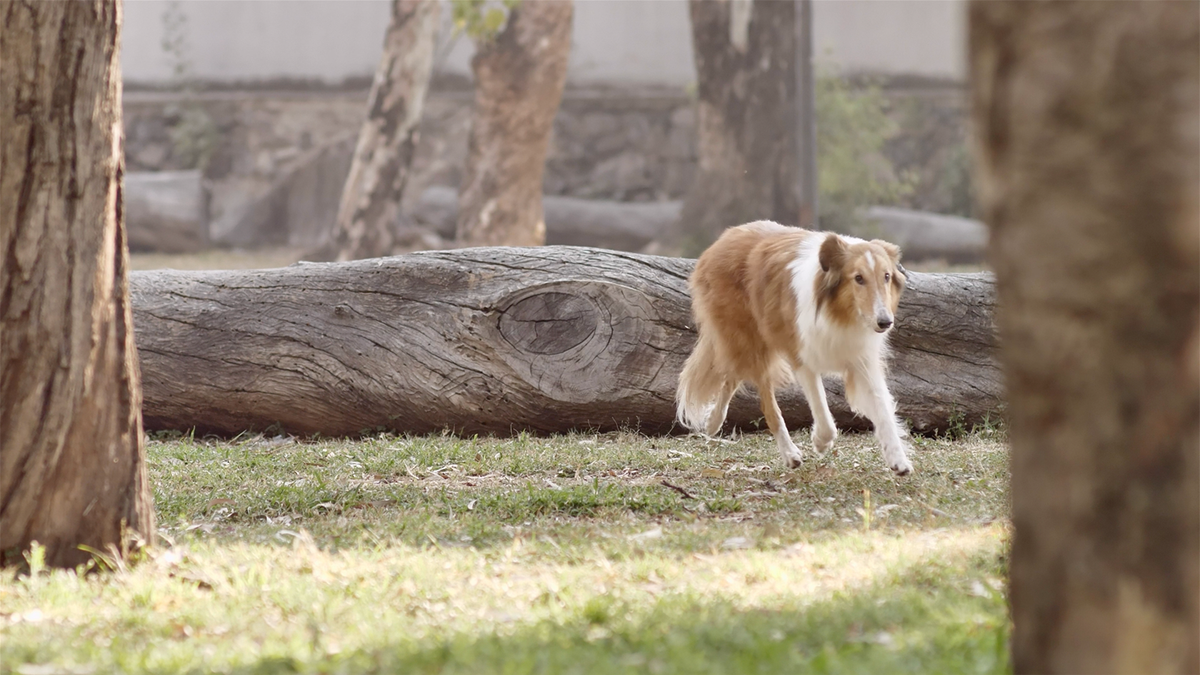



Wherever you are, whatever you do, you live in a soundscape; a mixture of sound events of different levels, durations, and texture. In the office you listen to the phone ringing, your keyboard keystrokes and your colleague speaking loudly. Walking down a path in the countryside, you listen to a gurgling stream, a birdsong and your footsteps. State-of-the-art deep learning approaches are able to recognise each single sound in a soundscape and then infer on the audio scene at hand.
Given a video, we employ cutting-edge matrix decomposition algorithms, referred to as low rank & sparse decomposition, to generate two new videos – one having the foreground, where the action is taking place, and the other having the slowly varying background fully recovered.
Named Entity Recognition (NER) – otherwise referred to as NER tagging - is a critical step towards language understanding and information extraction from unstructured text. NER aims at locating and classifying named entities (i.e. objects and concepts that can usually be denoted by nouns) into pre-defined categories from person names, organizations, locations, time objects to… food ingredients!
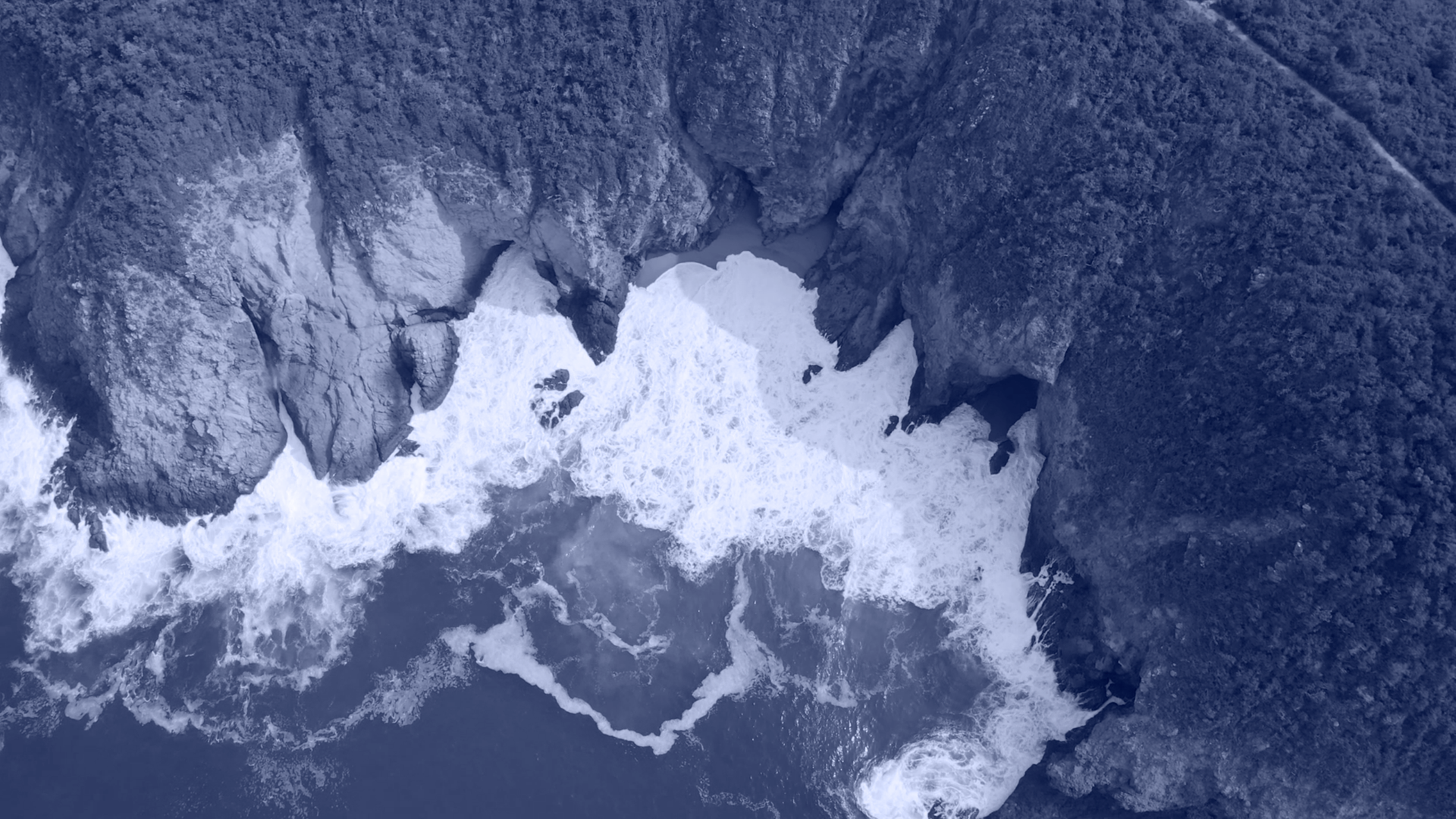
Segmentation of aerial and satellite imaging refers to classifying each single pixel of the image/map to a proper class. The advent of Deep Neural Networks significantly enhanced the performance of aerial map segmentation and land cover land use detection with numerous of applications.
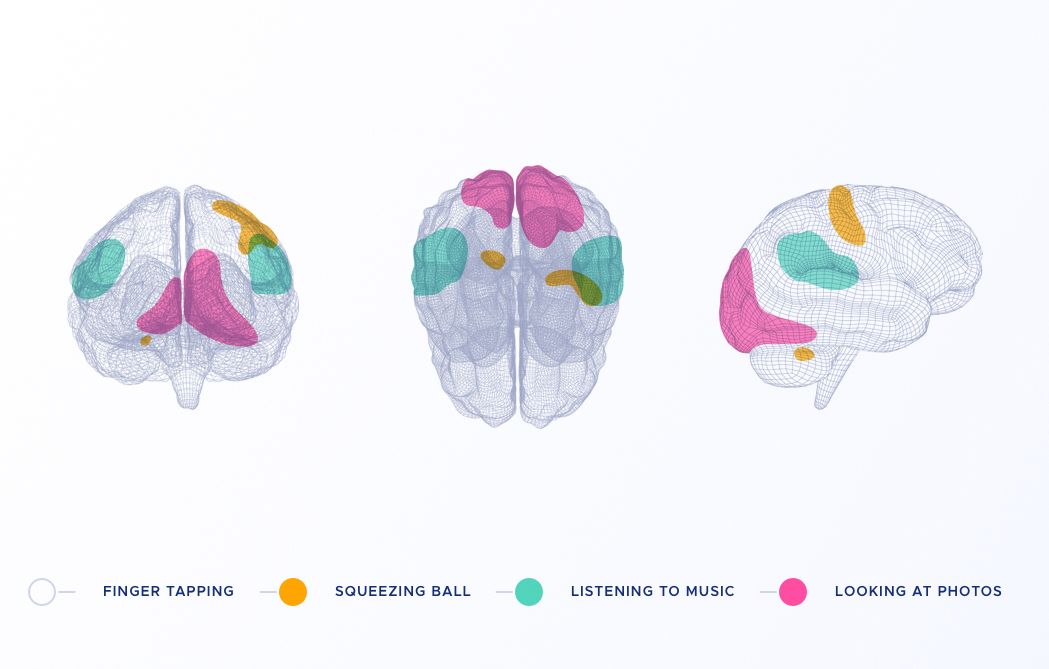
In order to perform several actions, the human brain relies on the simultaneous activation of many, so called, Functional Brain Networks (FBN), which are engaged in proper interactions to execute the tasks effectively. The FBNs appear as activated areas across the brain. It is important for many critical applications to invent methods that detect all FBNs accurately. From better understanding how human brain works to delineate areas that need to stay untouched in the case of a brain surgery to prevent severe counter effects. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is the dominant data acquisition technique for the detection and study of FBNs. However, in fMRI, FBNs appear mixed and highly overlapped and to isolate them is a very challenging problem. Modern Machine Learning brings novel competitive approaches in FBN unmixing.
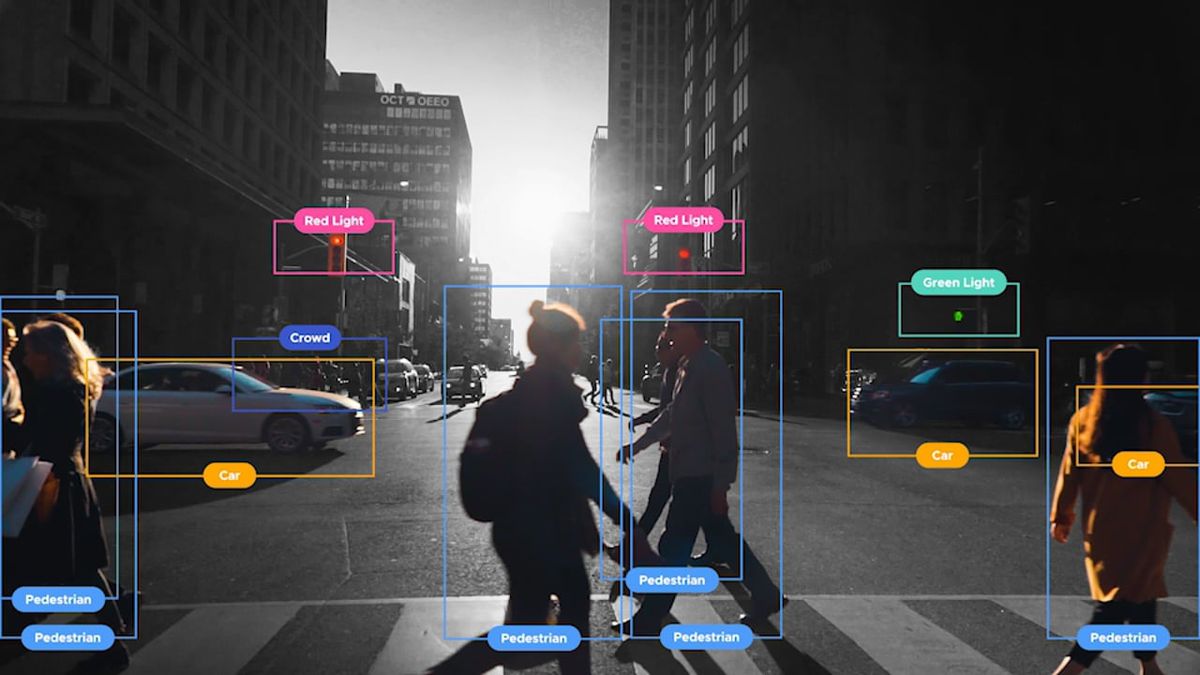
Deep learning technologies are a game changer in computer vision applications. Object detection is a major such application. It aims at detecting instances and locations of semantic objects of a certain class, e.g. a dog or a cat, in digital images or videos. Domain-specific object detection (e.g. automobile related classes) can lead disruptive novel applications
AI technologies
underpinning our work
 Machine Learning
Machine Learning
Allows mathematical models expressed through software applications to learn from data (or by example) and make predictions, understand previously unseen data, and identify patterns without being explicitly programmed.
 Deep learning
Deep learning
Machine Learning branch loosely inspired by the learning functionality of the biological brain and its neurons. It Involves the training of excessively large computational models that comprise millions of processing units organised in cascaded interconnected layers.
 Online Learning
Online Learning
Machine Learning typically requires all data to be collected and stored prior to training. Online learning offers techniques that train predictive models ‘on the fly’ by successively consuming streams of incoming data. Moreover, online learning naturally adapts to drifts of the conditions.
 Distributed & Federated Learning
Distributed & Federated Learning
When the training data are not collected in a single point but distributed in a number of places (e.g. mobile phones) then distributed learning is mobilised to train models in a decentralised fashion without requiring data to be transfered (preserving privacy and data safety).
 Robust Learning
Robust Learning
In realistic conditions, training data used to train ML models are likely to be partially corrupted, have missing entries and contain outliers. Robust learning approaches are resilient in such data deficiencies performing well even in harsh conditions.
 Novelty detection
Novelty detection
Refers to methods that they first learn what it can be considered as normality in the available data and then, they alert whenever an event or a dataset that looks different or surprising appears. In this way any change (positive or negative) in the behaviour of our customers or products can be promptly detected.
Wherever you are, whatever you do, you live in a soundscape; a mixture of sound events of different levels, durations, and texture. In the office you listen to the phone ringing, your keyboard keystrokes and your colleague speaking loudly. Walking down a path in the countryside, you listen to a gurgling stream, a birdsong and your footsteps. State-of-the-art deep learning approaches are able to recognise each single sound in a soundscape and then infer on the audio scene at hand.
Ham and Bananas HollandaiseRecipe
PeelPrep technique 6Number mediumSize bananasIngredient, spreadPrep technique 6Number thin slicesCut boiled hamIngredient (about 1/2 lbQuantity) with mustardIngredient and wrapPrep technique each bananaIngredient in sliceCut of hamIngredient. Arrange in single layer in casseroleEquipment. PreheatCooking tec. ovenEquipment to 400FTemperature and bakeCooking technique 10 minutesTime. Pour 1 ¼-ozQuantity hollandaise sauceIngredient over bananasIngredient. Nice with a green saladRecipe for brunchMeal or lunchMeal.
McCall'sName Great American Recipe Card Collection, 1973Date
-
Meal / cuisine
- Ingredients
- Recipe
- Meal
Click to interact
-
Prep & Cook
- Cooking technique
- Prep technique
- Cut style
- Equipment
-
General
- Size
- Number
- Quantity
- Name
- Date
- Temperature
- Time
Named Entity Recognition (NER) – otherwise referred to as NER tagging - is a critical step towards language understanding and information extraction from unstructured text. NER aims at locating and classifying named entities (i.e. objects and concepts that can usually be denoted by nouns) into pre-defined categories from person names, organizations, locations, time objects to… food ingredients!
Segmentation of aerial and satellite imaging refers to classifying each single pixel of the image/map to a proper class. The advent of Deep Neural Networks significantly enhanced the performance of aerial map segmentation and land cover land use detection with numerous of applications.
In order to perform several actions, the human brain relies on the simultaneous activation of many, so called, Functional Brain Networks (FBN), which are engaged in proper interactions to execute the tasks effectively. The FBNs appear as activated areas across the brain. It is important for many critical applications to invent methods that detect all FBNs accurately. From better understanding how human brain works to delineate areas that need to stay untouched in the case of a brain surgery to prevent severe counter effects. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is the dominant data acquisition technique for the detection and study of FBNs. However, in fMRI, FBNs appear mixed and highly overlapped and to isolate them is a very challenging problem. Modern Machine Learning brings novel competitive approaches in FBN unmixing.
Deep learning technologies are a game changer in computer vision applications. Object detection is a major such application. It aims at detecting instances and locations of semantic objects of a certain class, e.g. a dog or a cat, in digital images or videos. Domain-specific object detection (e.g. automobile related classes) can lead disruptive novel applications
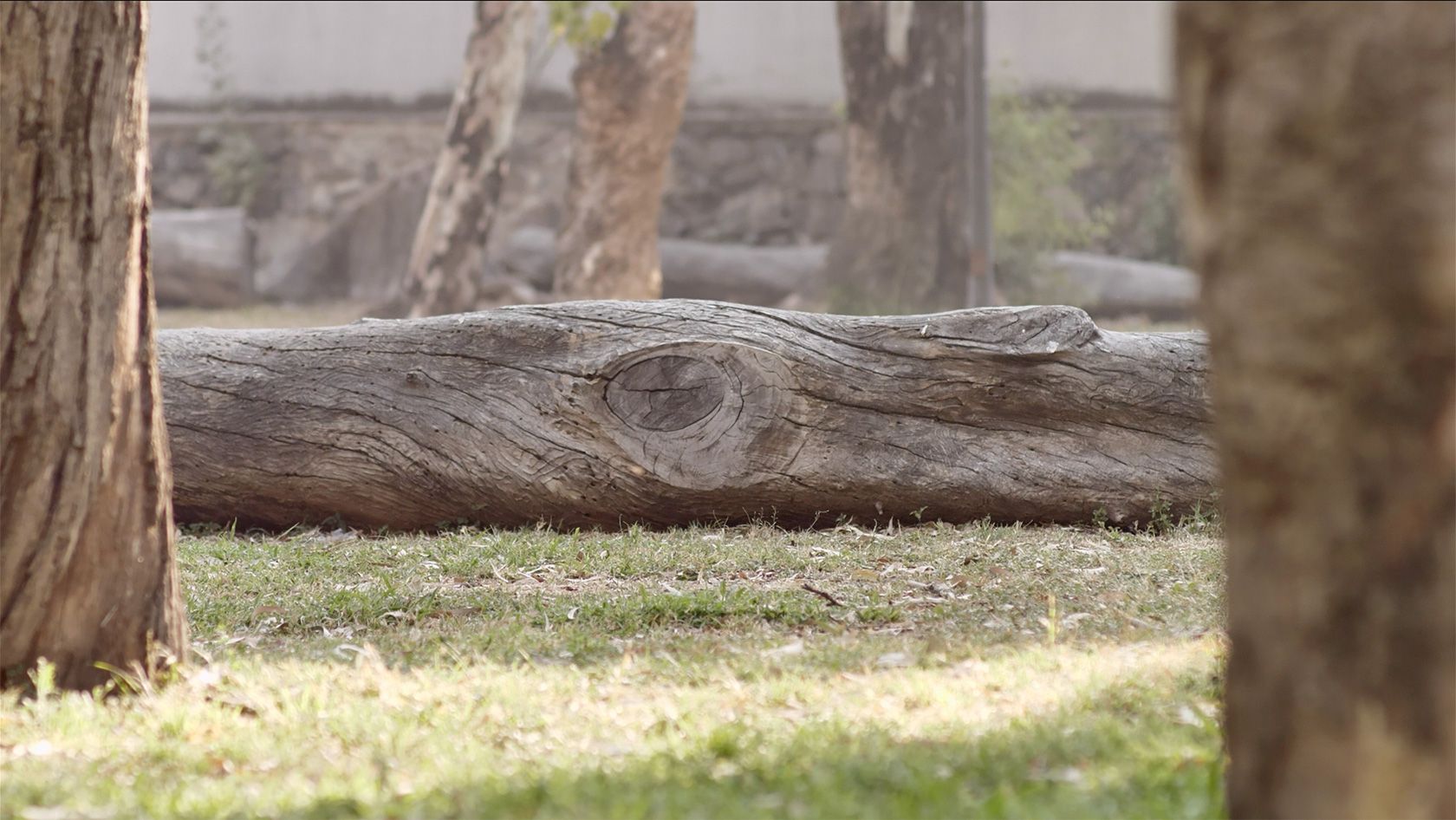
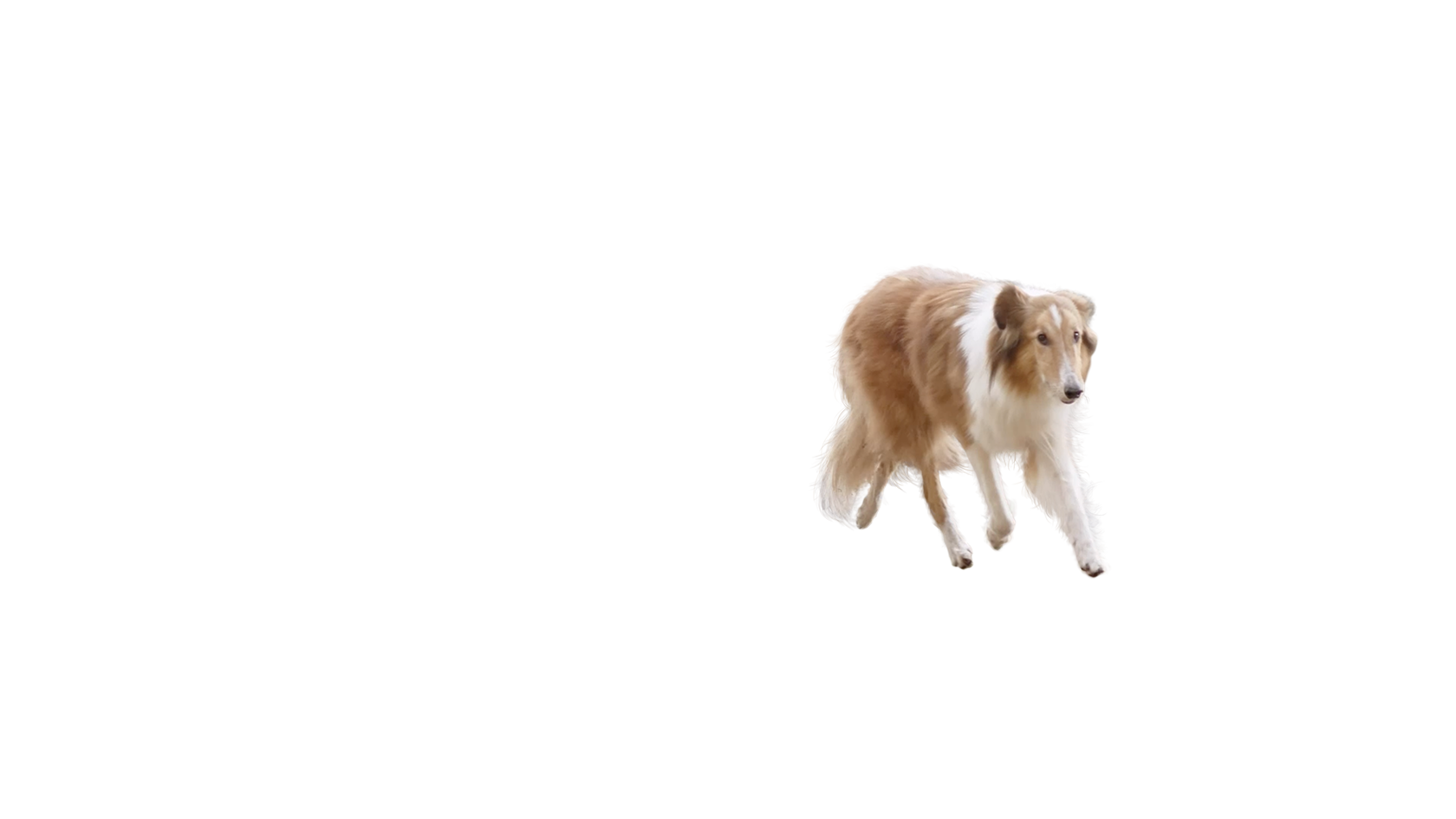


 Slide to interact
Slide to interact